Report builder API
System Reports
Introduction
System reports are a consistent way of providing reporting data, with paging, filtering, exporting standardized across them. Once the groundwork is done in defining the report elements in entities, it's possible to implement them with minimal code just by adding entities to the report, and defining which elements you want to use from them.
Column
Column overview
Column instances define the data captured/displayed within a report column typically:
- How the data is retrieved, either a simple SQL table.field fragment or an expression that returns a value
- They type of data that is being retrieved (int, text, datetime, etc)
- How that data should be presented in a report (for instance calling userdate() on datetime types)
Column types
TextInteger(Integer numbers)Float(Decimal numbers)Timestamp(Dates)Boolean(Yes / No values)Longtext
Creating columns
To create a new column, just create a new instance of reportbuilder/classes/local/report/column.php class with:
* string $name
* ?lang_string $title
* string $entityname
And use:
- add_joins() to add any extra SQL joins the column might need
- set_type() to add the column type (All constant types are defined within the same column class)
- set_is_sortable() to define if column can be sorted (For example we don't want to sort if the column shows just a picture)
- add_callback() to format the output of the column
- add_field() to add any db fields format callback might need
$columns[] = (new column(
'starttime',
new lang_string('task_starttime', 'admin'),
$this->get_entity_name()
))
->add_joins($this->get_joins())
->set_type(column::TYPE_TIMESTAMP)
->add_field("{$tablealias}.timestart")
->set_is_sortable(true)
->add_callback([format::class, 'userdate']);
Filter
Filter overview
Report filters can be defined for a report and allow users to narrow down (filter) the data that is displayed in a report:
- They define the data being filtered, either a simple SQL fragment or expression.
- The type of filtering being performed (int, text, datetime, etc). Filter types are extendable, allowing for the addition of many more as suit each use case. We have provided common ones that cover most use cases.
Filters & columns are entirely separate concepts in the report, and each can be used without a matching column/filter (that is to say, we can add a report filter for a user field without needing the column for the same field to be present in the report).
Filter types
- Text (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/text.php)
- Date (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/date.php)
- Number (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/number.php)
- Boolean Select (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/boolean_select.php)
- Select (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/select.php)
- Course selector (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/course_selector.php)
- Duration (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/duration.php)
- Tags (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/tags.php)
- Autocomplete (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/autocomplete.php)
- Category (reportbuilder/classes/local/filters/category.php)
Creating filters
To create a new filter, just create a new instance of reportbuilder/classes/local/report/filter.php class with:
* string $filterclass
* string $name
* lang_string $header
* string $entityname
* string $fieldsql = ''
* array $fieldparams = []
$filters[] = (new filter(
course_selector::class,
'courseselector',
new lang_string('courses'),
$this->get_entity_name(),
"{$tablealias}.id"
))
->add_joins($this->get_joins());
Entity
Entity overview
Entities are simply collections of report elements (currently columns and filters). They allow for common elements to be defined once, and then re-used in all reports - developers can choose to use as many or as few of the elements from each entity as required. We have provided user and course entities. They can be joined to reports using standard SQL query syntax.
All report elements can be defined within the reports themselves - but entities mean it's much easier to create re-usable components, and will also help in the long term with custom reports.
Create an entity
To create an entity, the new entity class must extend reportbuilder/classes/local/entities/base.php class and must include these methods:
get_default_table_aliases()
get_default_entity_title()
initialise()
get_default_table_aliases()
Defines the SQL alias for the database tables the entity uses.
get_default_entity_title()
Defines the default title for this entity.
initialise()
This is where we add the entity columns and filters.
Examples
Check out these two entities as an example to start building reports:
- User entity: reportbuilder/classes/local/entities/user.php
- Course entity: reportbuilder/classes/local/entities/course.php
Actions
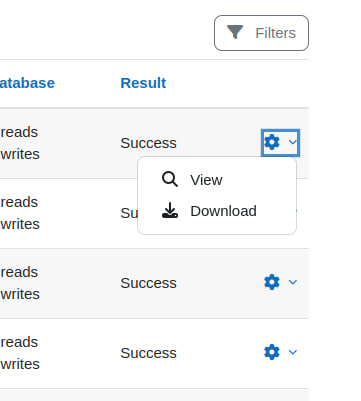
Report actions can be defined in system reports to provide CTA links for each row in the report. Using :placeholder elements in the action URLs allows them to be specific to the row content. For example, to always provide a link to the current user/course of the current row
$this->add_action((new action(
new moodle_url('/admin/tasklogs.php', ['logid' => ':id']),
new pix_icon('e/search', ''),
[],
true,
new lang_string('viewtasklog', 'report_tasklogs')
)));
System reports
System reports are a consistent way of providing reporting data, with paging, filtering, exporting standardized across them. Once the groundwork is done in defining the report elements in entities, it's possible to implement them with minimal code just by adding entities to the report, and defining which elements you want to use from them
Create a new system report using entities
To create a new system report just create a new class extending reportbuilder/classes/system_report.php.
The first method that we need is initialise() :
/**
* Initialise report, we need to set the main table, load our entities and set columns/filters
*/
protected function initialise(): void {
The initialise method needs to get the main entity, set the main table it needs to use and add the entity to the report:
// Our main entity, it contains all of the column definitions that we need.
$entitymain = new task_log();
$entitymainalias = $entitymain->get_table_alias('task_log');
$this->set_main_table('task_log', $entitymainalias);
$this->add_entity($entitymain);
After that, if the report will have 'Actions', it needs to define the columns these actions will use:
$this->add_base_fields("{$entitymainalias}.id");
Now, after adding our first entity, the report can use the columns and filters from it OR more entities can be added to the report using SQL joins:
$entityuser = new user();
$entituseralias = $entityuser->get_table_alias('user');
$this->add_entity($entityuser->add_join(
"LEFT JOIN {user} {$entituseralias} ON {$entituseralias}.id = {$entitymainalias}.userid"
));
Once all entities have been added it needs to define which columns it needs to show in the order we need:
$columns = [
'task_log:name',
'task_log:type',
'user:fullname',
'task_log:starttime',
];
$this->add_columns_from_entities($columns);
After defining the columns, it needs to define all the filters (or empty array for no filters) that it will use:
$filters = [
'task_log:name',
'task_log:result',
'task_log:timestart',
];
$this->add_filters_from_entities($filters);
In case it needs actions for each report row, they can be defined like:
// Action to download individual task log.
$this->add_action((new action(
new moodle_url('/admin/tasklogs.php', ['logid' => ':id', 'download' => true]),
new pix_icon('t/download', ''),
[],
new lang_string('downloadtasklog', 'report_tasklogs')
)));
Note that the placeholders used here (:id in this example) have been previously added using add_base_fields();
Once the whole report has been defined, is possible to set if the report will be downloadable or not:
$this->set_downloadable(true);
Use an entity
Override display name for a column
It's possible to override the display name of a column, if you don't want to use the value provided by the entity.
if ($column = $this->get_column('user:fullname')) {
$column->set_title(new lang_string('user', 'admin'));
}
Set a default initial sort direction
It's possible to set a default initial sort direction for one column.
$this->set_initial_sort_column('task_log:starttime', SORT_DESC);
Examples
Check out these two system reports as an example: